Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?
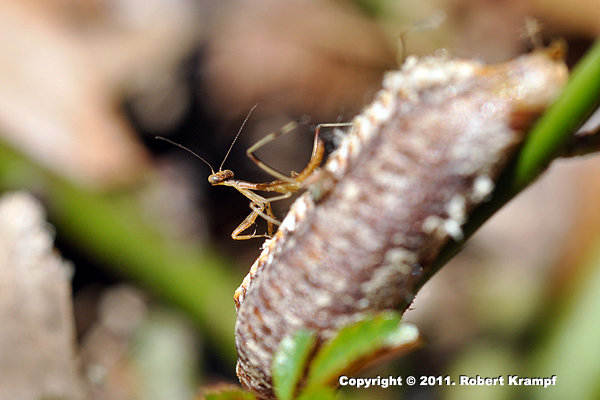

This baby praying mantis looks very much like its mother, but not exactly. What does that tell us about its life cycle?
-
It does not undergo metamorphosis.
No. While it does look similar to its parents, it lacks wings and other features which it will have as an adult. -
It has incomplete metamorphosis.
Yes! It has most of the features of an adult, and will gain the final adult features later in its life. -
It has complete metamorphosis.
No. For complete metamorphosis, the larva looks very different from the parent. -
It skipped metamorphosis.
No. While it does look similar to its parents, it lacks wings and other features which it will have as an adult.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.L.16.1 Observe and describe major stages in the life cycles of plants and animals, including beans and butterflies.
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.4 Compare and contrast the major stages in the life cycles of Florida plants and animals, such as those that undergo incomplete and complete metamorphosis, and flowering and nonflowering seedbearing
plants.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Creating a Sprout Guide | text page, photography, free |
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.5.V.1.c Compare various examples of offspring that do not initially resemble the parent organism but mature to become similar to the parent organism (e.g., mealworms and darkling beetles, tadpoles and frogs, seedlings and vegetables, caterpillars and butterflies).
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-4 | practice |
NGSS
1-LS3-1 Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that young plants and animals are like, but not exactly like, their parents.
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |
3-LS1-1 Develop models to describe that organisms have unique and diverse life cycles but all have in common birth, growth, reproduction, and death.
| Review Life Cycle-1 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-2 | practice |
| Review Life Cycle-3 | practice |

Which of the following observations is NOT scientifically testable?
-
Butterflies have pretty wings.
Yes! Pretty is an opinion, and can vary from person to person, so it is NOT scientifically testable. -
Butterflies have six legs.
No. This could be tested by counting the legs of a variety of butterflies. -
Butterflies can sting like bees.
No. A claim does not have to be true to be testable. Examination of a variety of butterflies would show that they do not have stingers. -
Most butterflies drink nectar from flowers.
No. This could be tested by observing the feeding habits of butterflies.
Explain more about it.
If I said that butterflies did not have six legs, you could show me physical evidence by counting their legs. After counting the legs, the physical evidence would show that butterflies have six legs.
If I said that I don't think butterfly wings are pretty, you could show me wings that you think are pretty, but I might not agree with your opinion. "Pretty" is not something that we can measure. What is pretty to one person might not be pretty to another, so it is not a testable property.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.2.1 Recognize and explain that science is grounded in empirical observations that are testable; explanation must always be linked with evidence.
| My Position on Science and Religion | video |
| What is Science?: Objective | video |
| Mobius Strip | video |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? | text page |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? Part 2 | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
SC.8.N.2.1 Distinguish between scientific and pseudoscientific ideas.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Feeding Bread to Birds | text page |
| Fact checking GMOs | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part four | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part three | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part two | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part one | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
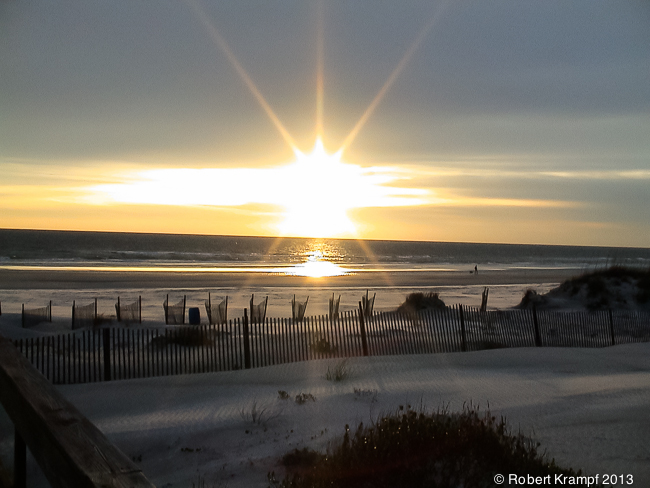

Which of the following states of matter will change its shape to fit its container, but not its size?
-
Solid
No. Under normal pressure, solids do not change their shape or size to fit their container. -
Liquid
Yes. Liquids will take on the shape of their container, but do not change their size. -
Gas
No. Gases will expand to fill their container, taking on both its shape and size. -
Plasma
No. Like gases, plasmas take on the size and shape of their container.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.P.8.3 Recognize that solids have a definite shape and that liquids and gases take the shape of their container.
| Egg States | video, checked |
| Wonderful Water | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
SC.5.P.8.1 Compare and contrast the basic properties of solids, liquids, and gases, such as mass, volume, color, texture, and temperature.
>>> Teacher Page: States of Matter
| Air Space | video |
| A Bouncing Water Balloon | video |
| Egg States | video, checked |
| Experimenting with Dry Ice | video, free, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Air has Weight | text page |
| Teach It Right the First Time. | text page, free |
| Review Matter-2 | practice |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
| Review Matter-3 | practice |
| Review Weather-10 | practice |
SC.8.P.8.1 Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by using models to explain the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases.
| A Bouncing Water Balloon | video |
| Egg States | video, checked |
| Experimenting with Dry Ice | video, free, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Expansion of Solids | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
| Review Matter-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.5.I.2.a Identify the physical properties of matter (e.g., hard, soft, solid, liquid, gas).
| Crushed Can | video, checked |
| A Bouncing Water Balloon | video |
| Egg States | video, checked |
| Experimenting with Dry Ice | video, free, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
| Review Matter-3 | practice |
UT.7.I.1.c Diagram the arrangement of particles in the physical states of matter (i.e., solid, liquid, gas).
| A Bouncing Water Balloon | video |
| Egg States | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
UT.8.I.1.b Classify substances based on their chemical and physical properties (e.g., reacts with water, does not react with water, flammable or nonflammable, hard or soft, flexible or nonflexible, evaporates or melts at room temperature).
| Wax and Wood, part 2 | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| Scaring Pepper | video, checked |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Relighting Candles | video, checked |
| How They Get the Sparks in a Sparkler | video |
| Orange Flash | video |
| Stale Bread | video |
| Cabbage Indicator | video, checked |
| Experimenting with Dry Ice | video, free, checked |
| Making Butter | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Wax and Wood, part 1 | video, checked |
| Acid Hunt | text page |
| A Clean Trick | text page |
| Review Matter-1 | practice |
NGSS
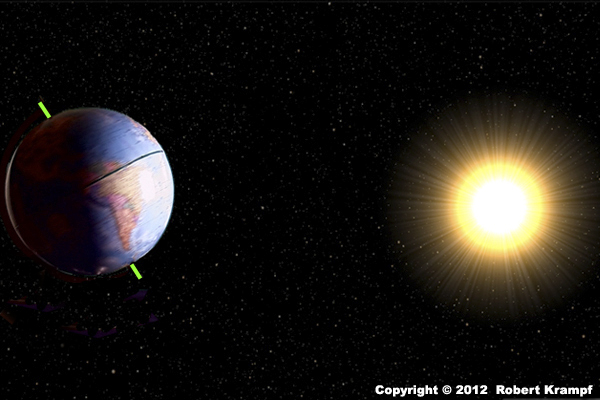
What season is Australia having in this graphic?
-
Spring
No. In the spring, the Earth's axis would not be tilted towards or away from the Sun. -
Summer
Yes! Australia is in the southern hemisphere, which is tilted towards the Sun. That tells us that it is summer there. -
Autumn
No. In the autumn, the Earth's axis would not be tilted towards or away from the Sun. -
Winter
No. Australia is in the southern hemisphere. If it was having winter, then the southern hemisphere would be tilted away from the Sun.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.5.1 Observe that the patterns of stars in the sky stay the same although they appear to shift across the sky nightly, and different stars can be seen in different seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.9 Explain the impact of objects in space on each other including: 1. the Sun on the Earth including seasons and gravitational attraction 2. the Moon on the Earth, including phases, tides, and eclipses, and the relative position of each body.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.II.2.e Use a model to explain why the seasons are reversed in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
NGSS
5-ESS1-2 Represent data in graphical displays to reveal patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Finding Your Way | video, checked |
| Review Space-5 | practice |
| Review Space-8 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
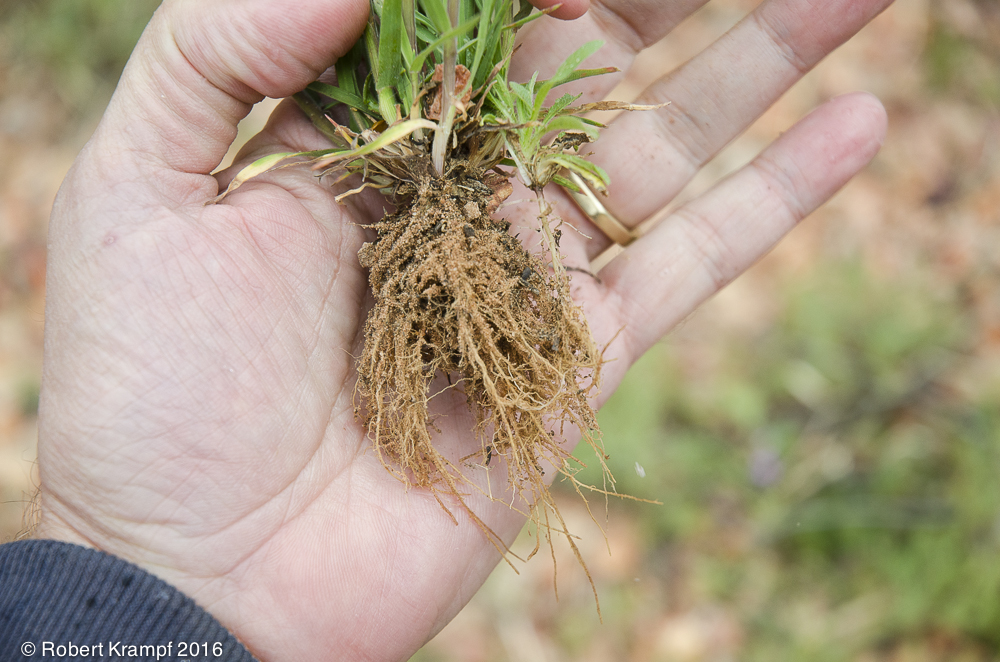

Which part of your body comes closest to serving the same function as a plant's roots?
-
Mouth
Yes! The main functions for most plant roots is to anchor it in place and to take in water and nutrients from the soil. We do not need anything to anchor us in one place, but we use our mouth to take in water and nutrients. -
Feet
No. A plants roots anchor into in place, keeping it from moving. Your feet do not do that. -
Lungs
No. A plant takes in air through its leaves, not through its roots. -
Skeleton
No. Your skeleton supports your body and protects your organs. In plants, this is done by the cell walls. The cell wall around each cell of a plant make it stiff, supporting stems, leaves, flowers, and other parts of the plant.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.14.1 Describe structures in plants and their roles in food production, support, water and nutrient transport, and reproduction.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Heartless Plants | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Smell the Flowers | text page |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.1 Identify processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including pollination, fertilization (seed production), seed dispersal, and germination.
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
SC.5.L.14.2 Compare and contrast the function of organs and other physical structures of plants and animals, including humans, for example: some animals have skeletons for support — some with internal skeletons others with exoskeletons — while some plants have stems for support.
| Bird Bones | video, free |
| Reading a Skeleton | video, free, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.V.1.b Compare characteristics common in observed organisms (e.g., color, movement, appendages, shape) and infer their function (e.g., green color found in organisms that are producers, appendages help movement).
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
UT.7.IV.2.d Relate the structure of organs to an organism’s ability to survive in a specific environment (e.g., hollow bird bones allow them to fly in air, hollow structure of hair insulates animals from hot or cold, dense root structure allows plants to grow in compact soil, fish fins aid fish in moving in water).
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Hunting with an Umbrella | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Bendable Bones | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS1-1 Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that living things are made of cells; either one cell or many different numbers and types of cells.
| Microscopes: Making a Hay Infusion | video, free, learnalong, checked |
| Microscopes: Making a Wet Mount | video, learnalong, checked |
| Microscopes: Making a Dry Mount | video, learnalong, checked |
| 901 | photo challenge, free |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
