Here are some science questions to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
Back to the Grade 5 standards.

Which of the following observations is scientifically testable?
-
Honeybees are good insects.
No. "Good" is a generic term that could mean many different things in different situations. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are important insects.
No. "Important" is a generic term that could mean many different things to different people. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are pretty insects.
No. Some people might think that a honeybee is pretty, and some people might not. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are not insects.
Yes! While this statement is not correct, it is scientifically testable. You could examine the bee to see that it does fit the definition of an insect. This statement is IS scientifically testable.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.2.1 Recognize and explain that science is grounded in empirical observations that are testable; explanation must always be linked with evidence.
| My Position on Science and Religion | video |
| What is Science?: Objective | video |
| Mobius Strip | video |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? | text page |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? Part 2 | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
SC.8.N.2.1 Distinguish between scientific and pseudoscientific ideas.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Feeding Bread to Birds | text page |
| Fact checking GMOs | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part four | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part three | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part two | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part one | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
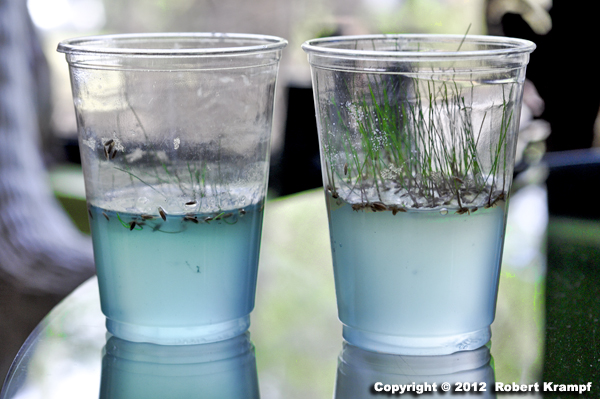
I wanted to test different amounts of fertilizer to see which was best for growing grass. I mixed water with different amounts of fertilizer, and then added sodium polyacrylate to change it into a gel. Then I sprinkled the grass seeds on top, and waited for them to grow.
I really need a control group for this experiment. What would I use for a control?
-
Water, fertilizer, and grass seed, without any sodium polyacrylate.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of sodium polyacrylate. -
Water, sodium polyacrylate, and grass seed, without any fertilizer.
Yes! We are testing to see how different amounts of fertilizer change the growth of the grass. The amount of fertilizer is the variable we are testing, so the control group should not have any fertilizer. -
Water, sodium polyacrylate, and fertilizer, without any grass seed.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of grass seed, and we know that no grass will grow if we do not have any seeds. -
Sodium polyacrylate, fertilizer, and grass seed, without any water.
No. For the control, we want to skip the thing we are testing for. We are not testing changes caused by the amount of water.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
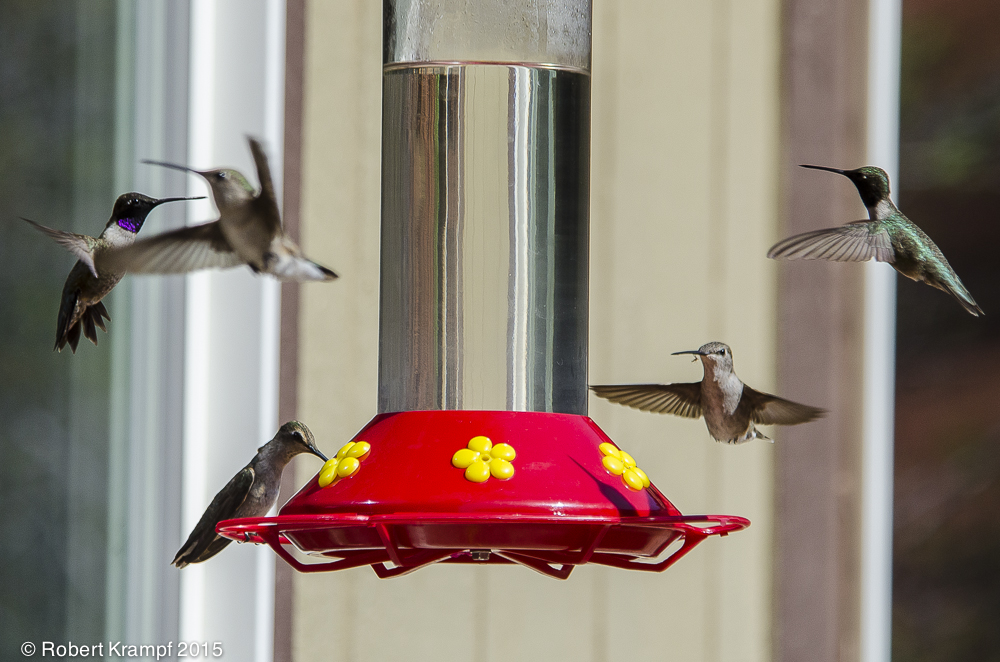

We enjoy the hummingbirds that visit our feeders. I am trying to find the mixture of sugar and water that they like the best.
Each day, I put out four feeders with different amounts of water and sugar. At the end of each day, I measure to see how much of each the hummingbirds drank. Which of the following is NOT an important part of this experiment?
-
One of the feeders should only contain water, with no sugar.
No. This IS an important part of the experiment. The feeder without any sugar is the control. If the hummingbirds drink just as much pure water, it would indicate that the sugar is not important. -
The feeders should be placed randomly every day.
No. This IS an important part of the experiment. If you always put the same mixture in the same location, the results may be because the birds like that location instead of because they like the amount of sugar. -
I should repeat this experiment every day for several weeks.
No. This IS an important part of the experiment. The more times you repeat the same test, the more likely you are to get accurate results. -
The different mixtures should be colored different colors with nontoxic food coloring.
Yes. This is NOT an important part of the experiment. It would add a second variable to the experiment, which is a bad thing. You want everything to be the same for each sample, with the only difference being the amount of sugar. If you used different colors and different amounts of sugar, you would not know whether the results were due to the color or the sugar.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |

What do you have to do to replicate an experiment?
-
You do the same experiment several times.
No. Doing the same experiment several times is repetition, not replication. -
You do the same experiment that someone else did.
Yes. By replicating an experiment exactly, you should get the same results as the original experiment. -
You do an improved version of someone's experiment.
For replication, you do the experiment exactly as the original scientist did, without making any changes. -
You look for errors in someone's experiment.
The purpose of replication is to verify, not to look for errors.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.N.1.4 Explain how particular scientific investigations should yield similar conclusions when repeated.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.5.N.2.2 Recognize and explain that when scientific investigations are carried out, the evidence produced by those investigations should be replicable by others.
>>> Teacher Page: Nature of Science and Dissolving
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.6.N.1.2 Explain why scientific investigations should be replicable.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.2 Differentiate replication (by others) from repetition (multiple trials).
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.8.N.1.2 Design and conduct a study using repeated trials and replication.
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
Utah
NGSS

I want to test a new fertilizer, to find the best concentration for my garden. To do this, I plan to divide my garden into four sections.
Section A. I will use 5 grams of fertilizer per gallon each time I fertilize.
Section B. I will use 10 grams of fertilizer per gallon each time I fertilize.
Section C. I will use 15 grams of fertilizer per gallon each time I fertilize.
For section D, how much fertilizer per gallon should I use?
-
20 grams of fertilizer per gallon.
No. This would be a good thing to test, but for this to be a proper science experiment, it is not the correct answer. -
30 grams of fertilizer per gallon.
No. This would be a good thing to test, but for this to be a proper science experiment, it is not the correct answer. -
1 gram of fertilizer per gallon.
No. This would be a good thing to test, but for this to be a proper science experiment, it is not the correct answer. -
No fertilizer at all.
Yes. For this type of experiment, you need to have a control group. That is a group of test subjects that you do not do anything to. If the control group with no fertilizer grows just as well as the other groups, then I would know that the fertilizer was not working.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
