Here are some science questions from the Standards for Grades 2-5 to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.

How hot does an area have to be to be classified as a desert?
Answer:
Deserts are defined by lack of precipitation, not by temperature. They are areas where precipitation minus evaporation yields less than 10 inches of rain per year. The largest desert on Earth is in Antarctica, a very cold place.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.E.7.6 Describe characteristics (temperature and precipitation) of different climate zones as they relate to latitude, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water.
| Weather and Climate | video |
| Review Weather-7 | practice |
| Review Weather-9 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.1.c Locate examples of areas that have characteristics of wetlands, forests, or deserts in Utah.
| Review Weather-7 | practice |
| Review Weather-9 | practice |
NGSS

This wasp is hunting the caterpillars that are eating this plant. Which of these is NOT a consumer?
-
The plant
Yes! The plant is a producer, not a consumer. Producers make their own food. -
The caterpillar
No. The caterpillar is a consumer because it eats the plant. -
The plant and the caterpillar
No. The caterpillar is a consumer. -
The caterpillar and the wasp
No. Consumers eat other organisms. Both the caterpillar and the wasp consume other living things, making them both consumers.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |

These building stones are made of a rock called coquina. The rock is almost entirely made up of pieces of fossil sea shells. What kind of rock is it?
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. That would have melted and destroyed the fossil shells. This is not an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. These bits of shell were deposited by water, so coquina is a Sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Coquina has not been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock, so it is not metamorphic. -
Coquina is not a rock.
No. Coquina is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Coquina is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |

A lightning bolt has a huge amount of energy. Which of these kinds of energy is NOT a major component of lightning?
-
Heat
No. A lightning bolt can heat the air to over 30,000 °C (54,000 °F) -
Electrical
No. A lightning bolt has a tremendous amount of electrical energy, often several hundred million volts, and several hundred thousand amperes. -
Sound
No. Thunder, the sound energy produced by a lightning bolt, is so loud that it can often be heard up to ten miles away. -
Chemical
Yes. While a lightning bolt can cause chemical changes, very little of the bolt's energy is converted to chemical energy.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.P.10.1 Observe and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, and the energy of motion.
| Electrostatic Charges | video |
| Noisy String | video, checked |
| Spoon Bells | video, checked |
| Making a Screamer | video, free, Updated |
| The Singing Glass | video, checked |
| Whistle Stick | video, text page, blog, free, checked |
| Review Energy-5 | quest |
| Review Energy-2 | practice |
SC.4.P.10.1 Observe and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, and the energy of motion.
| Electricity | video, free, Updated |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Measuring Kinetic and Potential Energy | video, checked |
| Electrostatic Charges | video |
| Why Things Go Bang | video |
| Noisy String | video, checked |
| Spoon Bells | video, checked |
| The Singing Glass | video, checked |
| Radioactive | video, Updated, checked |
| Bean Power | text page |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| Review Energy-5 | quest |
| Review Energy-2 | practice |
SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical.
| Making a Screamer | video, free, Updated |
| The Singing Glass | video, checked |
| Radioactive | video, Updated, checked |
| Electricity | video, free, Updated |
| The Science of Pizza | video, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Measuring Kinetic and Potential Energy | video, checked |
| Solar Power | video, checked |
| Why Things Go Bang | video |
| Sunglass Science: Birefringence | video, free, Updated |
| Noisy String | video, checked |
| Spoon Bells | video, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| Review Energy-5 | quest |
| Review Energy-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.IV.4.b Trace the conversion of energy from one form of energy to another (e.g., light to chemical to mechanical).
| Measuring Kinetic and Potential Energy | video, checked |
| The Rollback Can | video, free, Updated |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
NGSS
4-PS3-2 Make observations to provide evidence that energy can be transferred from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents.
| Bottle Tones, part 2 | video, checked |
| Why Things Go Bang | video |
| Noisy String | video, checked |
| Spoon Bells | video, checked |
| Making a Screamer | video, free, Updated |
| The Singing Glass | video, checked |
| Electricity | video, free, Updated |
| The Science of Pizza | video, checked |
| Heating a Balloon | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Simple Circuits | video, checked |
| Doppler Effect | video, checked |
| How Heat Moves | video, checked |
| Solar Power | video, checked |
| Bottle Tones, part 1 | video, checked |
| A Real Tuning Fork | text page |
| Comparing How Sound Moves Through Liquids and Gases | text page |
| Review Energy-2 | practice |
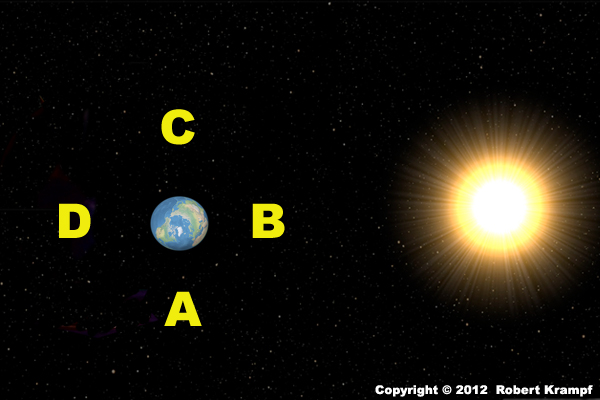
Which position would the Moon be in during an eclipse of the Moon?
-
A
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
B
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
C
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
D
Yes. In this position, the Moon could be in the Earth's shadow. It does not always pass through the shadow, so we don't have an eclipse every month, but when it does, it will be in this position.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.5.2 Describe the changes in the observable shape of the moon over the course of about a month.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.I.1.b Explain that the sun is the source of light that lights the moon.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
UT.6.I.1.a Describe changes in the appearance of the moon during a month.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
