Here are some science questions from the Standards for Grades 2-5 to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.

In the Yeast and Sugar video, I added different kinds of sugar to bottles with yeast and warm water. One of the bottles was a control. What should have been in that bottle?
-
Just water
No. With just water, you are removing two variables, the yeast and the sugar. You only want to remove the independent variable.
-
Water and yeast
Yes! A control should be exactly like the others, but without the independent variable (the variable you are changing in the experiment.) In this case, the variable you are changing is the kind of sugar, so the control should have everything except for the sugar. -
Water and sugar
No. The yeast is not the independent variable, so leaving it out would not be correct. -
Water and salt
No. Adding salt would be adding a new variable, which is not correct.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
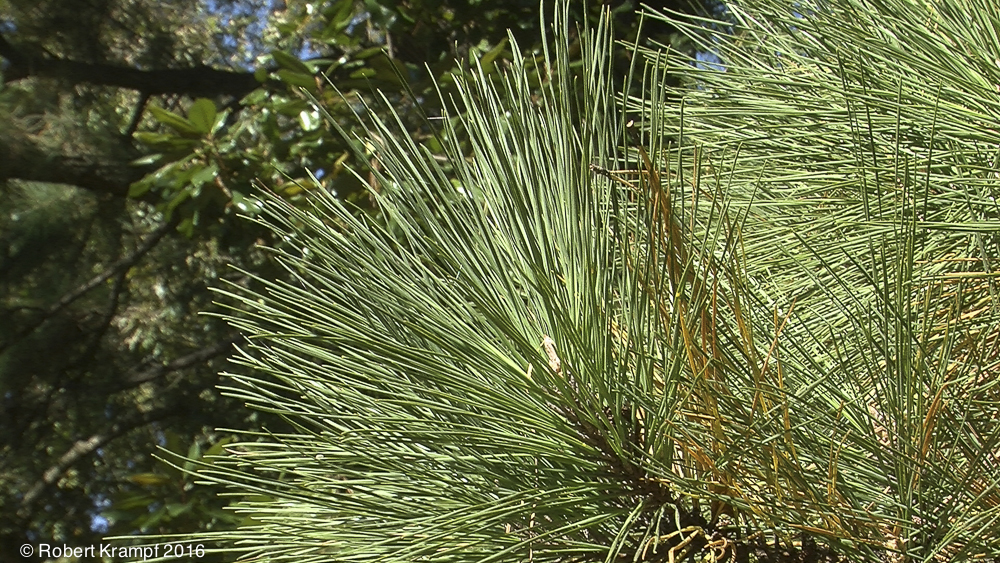

Pine trees do not have flowers. What structure do they have that servers the same purpose?
-
Needles
No. Pine needles are a kind of leaf. They are not used for reproduction. -
Cones
Yes! Pine cones produce pollen and seeds, just as flowers do in flowering plants. -
Fruit
No. Fruit are used for dispersing seeds, not for pollination. -
Buds
No. Pine tree buds produce needles. They are not involved in reproduction.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.3.L.15.2 Classify flowering and nonflowering plants into major groups such as those that produce seeds, or those like ferns and mosses that produce spores, according to their physical characteristics.
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
SC.3.L.14.1 Describe structures in plants and their roles in food production, support, water and nutrient transport, and reproduction.
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Heartless Plants | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Smell the Flowers | text page |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
SC.4.L.16.1 Identify processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including pollination, fertilization (seed production), seed dispersal, and germination.
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
4-LS1-1 Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction.
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bird Bones | video, free |
| Feathers | video, checked |
| Heartless Plants | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Eye Shine | text page |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Review Plants-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
| Review Plants-5 | practice |
| Review Plants-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-7 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively.
| Orange Slices | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Pumpkin Guts | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| How Does a Butterfly Fly? | text page, free |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Plants-2 | practice |
| Review Plants-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
| Review Plants-8 | practice |
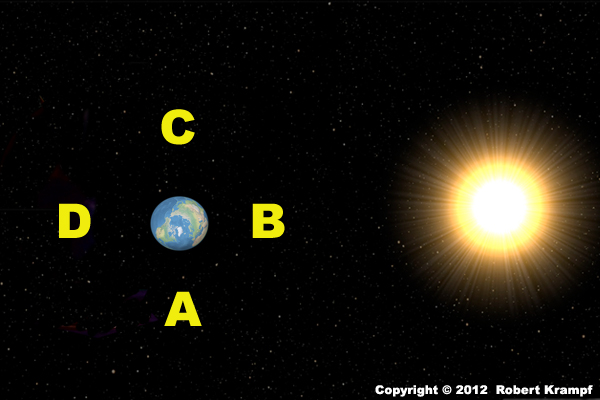
Which position would the Moon be in during an eclipse of the Moon?
-
A
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
B
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
C
No. In this position, the Moon would not be in the Earth's shadow. -
D
Yes. In this position, the Moon could be in the Earth's shadow. It does not always pass through the shadow, so we don't have an eclipse every month, but when it does, it will be in this position.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.5.2 Describe the changes in the observable shape of the moon over the course of about a month.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.I.1.b Explain that the sun is the source of light that lights the moon.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
UT.6.I.1.a Describe changes in the appearance of the moon during a month.
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-1 Develop and use a model of the Earth-sun-moon system to describe the cyclic patterns of lunar phases, eclipses of the sun and moon, and seasons.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-6 | practice |
| Review Space-7 | practice |
| Review Space-9 | practice |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
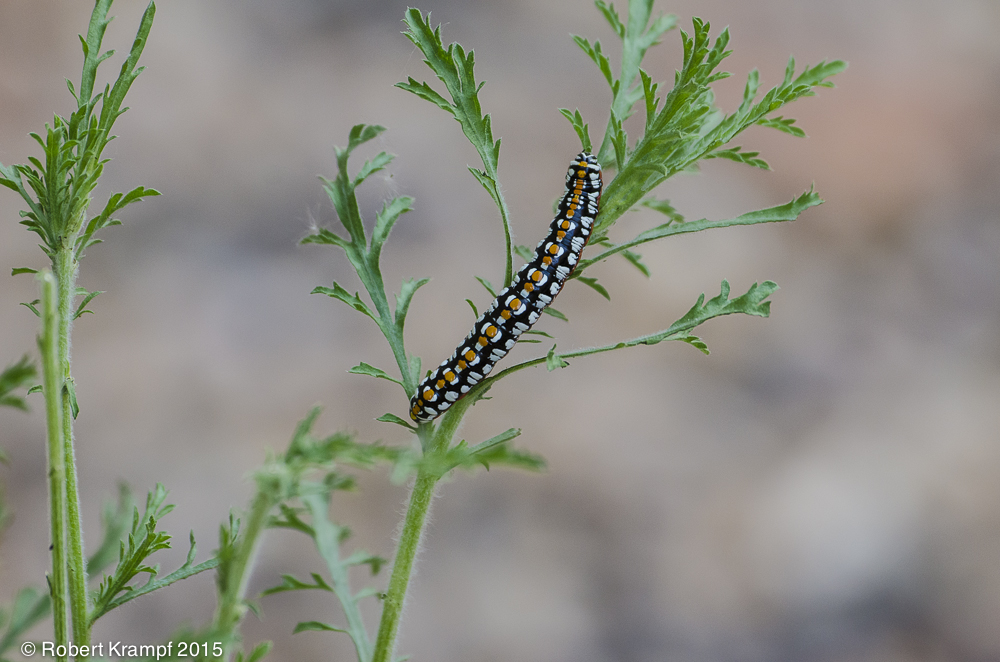

This caterpillar is an example of which part of the food web?
-
Producer.
No. The plant is a producer. It captures energy from sunlight, and stores it as food. The caterpillar is eating the plant to get that energy. -
Primary Consumer.
Yes! The caterpillar is eating the plant (a producer) to get the energy that is stored in its leaves. -
Secondary Consumer
No. Secondary consumers eat other consumers. A bird that ate this caterpillar would be a secondary consumer. -
Decomposer
No. Decomposers break down dead and decaying organisms. The plant that the caterpillar is eating is still alive and growing.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
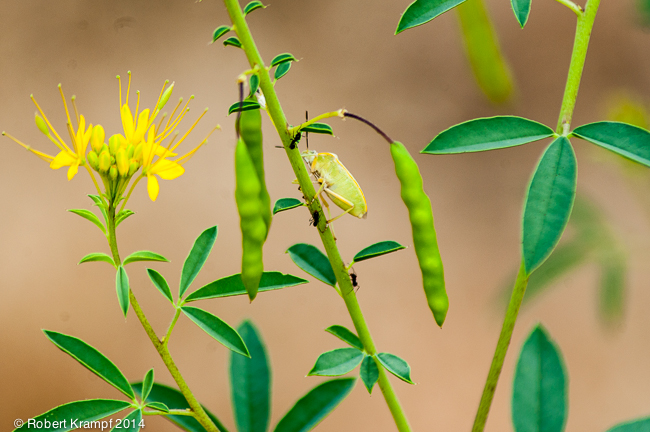

The large, green stinkbug is drinking sap from this plant. That tells us that it is a:
-
Producer.
No. The plant is a producer. It captures energy from sunlight, and stores it as food. The stinkbug is eating the plant to get that energy. -
Primary Consumer.
Yes! The stinkbug is eating the sap from the plant (a producer) to get the energy it contains. -
Secondary Consumer
No. Secondary consumers eat other consumers. An animal that ate this stinkbug would be a secondary consumer. -
Decomposer
No. Decomposers break down dead and decaying organisms. The plant that the stinkbug is eating is still alive and growing.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
